Plot Interaction Effects in a SEM Model
plot_interaction.RdThis function creates an interaction plot of the outcome variable (y) as a function
of a focal predictor (x) at multiple values of a moderator (z). It is
designed for use with structural equation modeling (SEM) objects (e.g., those from
modsem). Predicted means (or predicted individual values) are calculated
via simple_slopes, and then plotted with ggplot2 to display
multiple regression lines and confidence/prediction bands.
Usage
plot_interaction(
x,
z,
y,
model,
vals_x = seq(-3, 3, 0.001),
vals_z,
alpha_se = 0.15,
digits = 2,
ci_width = 0.95,
ci_type = "confidence",
rescale = TRUE,
standardized = FALSE,
xz = NULL,
greyscale = FALSE,
...
)Arguments
- x
A character string specifying the focal predictor (x-axis variable).
- z
A character string specifying the moderator variable.
- y
A character string specifying the outcome (dependent) variable.
- model
An object of class
modsem_pi,modsem_da,modsem_mplus, or possibly alavaanobject. Must be a fitted SEM model containing paths fory ~ x + z + x:z.- vals_x
A numeric vector of values at which to compute and plot the focal predictor
x. The default isseq(-3, 3, .001), which provides a relatively fine grid for smooth lines. Ifrescale=TRUE, these values are in standardized (mean-centered and scaled) units, and will be converted back to the original metric in the internal computation of predicted means.- vals_z
A numeric vector of values of the moderator
zat which to draw separate regression lines. Each distinct value invals_zdefines a separate group (plotted with a different color). Ifrescale=TRUE, these values are also assumed to be in standardized units.- alpha_se
A numeric value in \([0, 1]\) specifying the transparency of the confidence/prediction interval ribbon. Default is
0.15.- digits
An integer specifying the number of decimal places to which the moderator values (
z) are rounded for labeling/grouping in the plot.- ci_width
A numeric value in \((0,1)\) indicating the coverage of the confidence (or prediction) interval. The default is
0.95for a 95% interval.- ci_type
A character string specifying whether to compute
"confidence"intervals (for the mean of the predicted values, default) or"prediction"intervals (which include residual variance).- rescale
Logical. If
TRUE(default),vals_xandvals_zare interpreted as standardized units, which are mapped back to the raw scale before computing predictions. IfFALSE,vals_xandvals_zare taken as raw-scale values directly.- standardized
Should coefficients be standardized beforehand?
- xz
A character string specifying the interaction term (
x:z). IfNULL, the term is created automatically aspaste(x, z, sep = ":"). Some SEM backends may handle the interaction term differently (for instance, by removing or modifying the colon), and this function attempts to reconcile that internally.- greyscale
Logical. If
TRUEthe plot is plotted in greyscale.- ...
Additional arguments passed on to
simple_slopes.
Value
A ggplot object that can be further customized (e.g., with
additional + theme(...) layers). By default, it shows lines for each
moderator value and a shaded region corresponding to the interval type
(confidence or prediction).
Details
Computation Steps:
Calls
simple_slopesto compute the predicted values ofyat the specified grid ofxandzvalues.Groups the resulting predictions by unique
z-values (rounded todigits) to create colored lines.Plots these lines using
ggplot2, adding ribbons for confidence (or prediction) intervals, with transparency controlled byalpha_se.
Interpretation:
Each line in the plot corresponds to the regression of y on x at
a given level of z. The shaded region around each line (ribbon) shows
either the confidence interval for the predicted mean (if ci_type =
"confidence") or the prediction interval for individual observations (if
ci_type = "prediction"). Where the ribbons do not overlap, there is
evidence that the lines differ significantly over that range of x.
Examples
# \dontrun{
library(modsem)
# Example 1: Interaction of X and Z in a simple SEM
m1 <- "
# Outer Model
X =~ x1 + x2 + x3
Z =~ z1 + z2 + z3
Y =~ y1 + y2 + y3
# Inner Model
Y ~ X + Z + X:Z
"
est1 <- modsem(m1, data = oneInt)
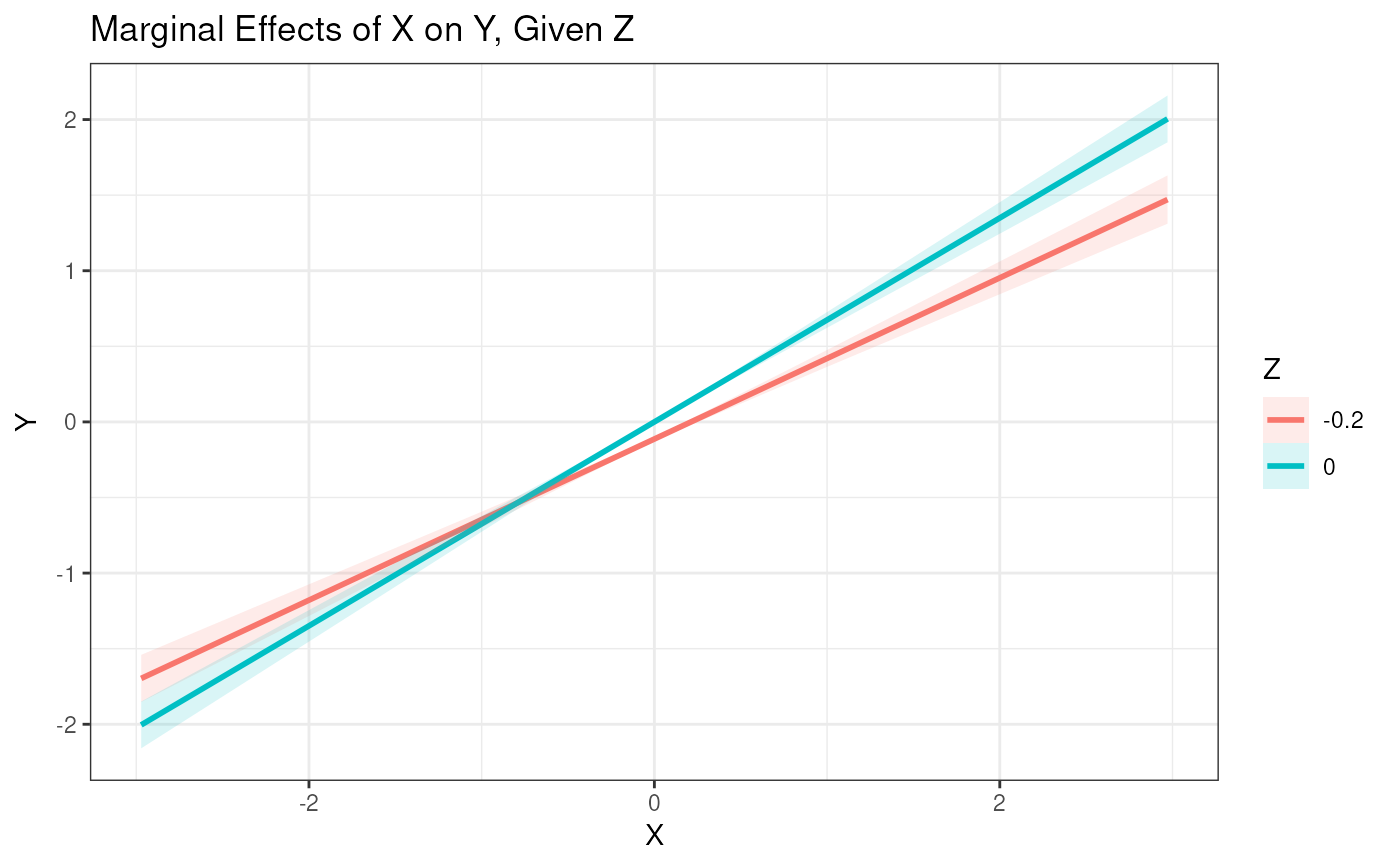
# Plot interaction using a moderate range of X and two values of Z
plot_interaction(x = "X", z = "Z", y = "Y", xz = "X:Z",
vals_x = -3:3, vals_z = c(-0.2, 0), model = est1)
 # Example 2: Interaction in a theory-of-planned-behavior-style model
tpb <- "
# Outer Model
ATT =~ att1 + att2 + att3 + att4 + att5
SN =~ sn1 + sn2
PBC =~ pbc1 + pbc2 + pbc3
INT =~ int1 + int2 + int3
BEH =~ b1 + b2
# Inner Model
INT ~ ATT + SN + PBC
BEH ~ INT + PBC
BEH ~ PBC:INT
"
est2 <- modsem(tpb, data = TPB, method = "lms", nodes = 32)
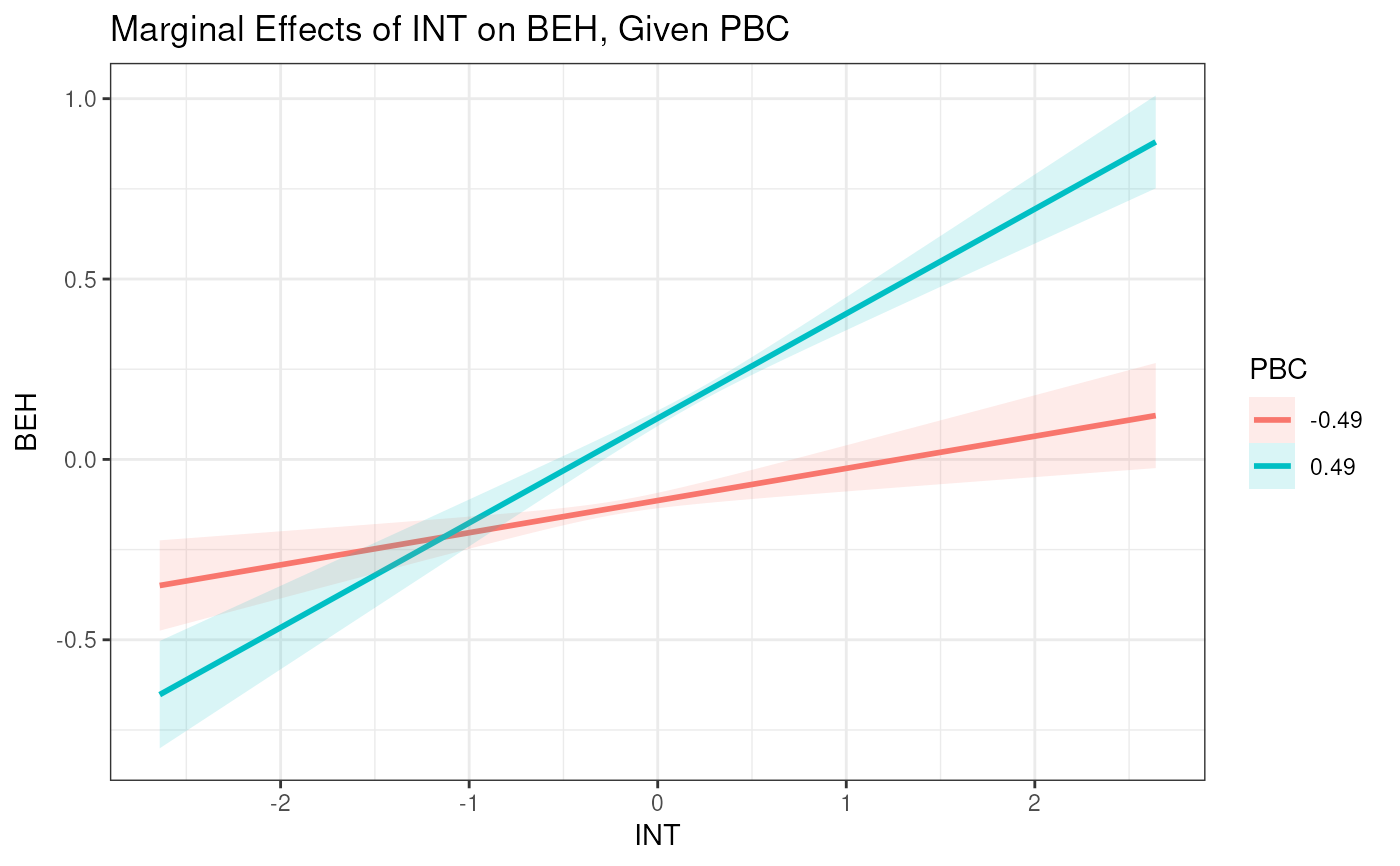
# Plot with custom Z values and a denser X grid
plot_interaction(x = "INT", z = "PBC", y = "BEH",
xz = "PBC:INT",
vals_x = seq(-3, 3, 0.01),
vals_z = c(-0.5, 0.5),
model = est2)
# Example 2: Interaction in a theory-of-planned-behavior-style model
tpb <- "
# Outer Model
ATT =~ att1 + att2 + att3 + att4 + att5
SN =~ sn1 + sn2
PBC =~ pbc1 + pbc2 + pbc3
INT =~ int1 + int2 + int3
BEH =~ b1 + b2
# Inner Model
INT ~ ATT + SN + PBC
BEH ~ INT + PBC
BEH ~ PBC:INT
"
est2 <- modsem(tpb, data = TPB, method = "lms", nodes = 32)
# Plot with custom Z values and a denser X grid
plot_interaction(x = "INT", z = "PBC", y = "BEH",
xz = "PBC:INT",
vals_x = seq(-3, 3, 0.01),
vals_z = c(-0.5, 0.5),
model = est2)
 # }
# }